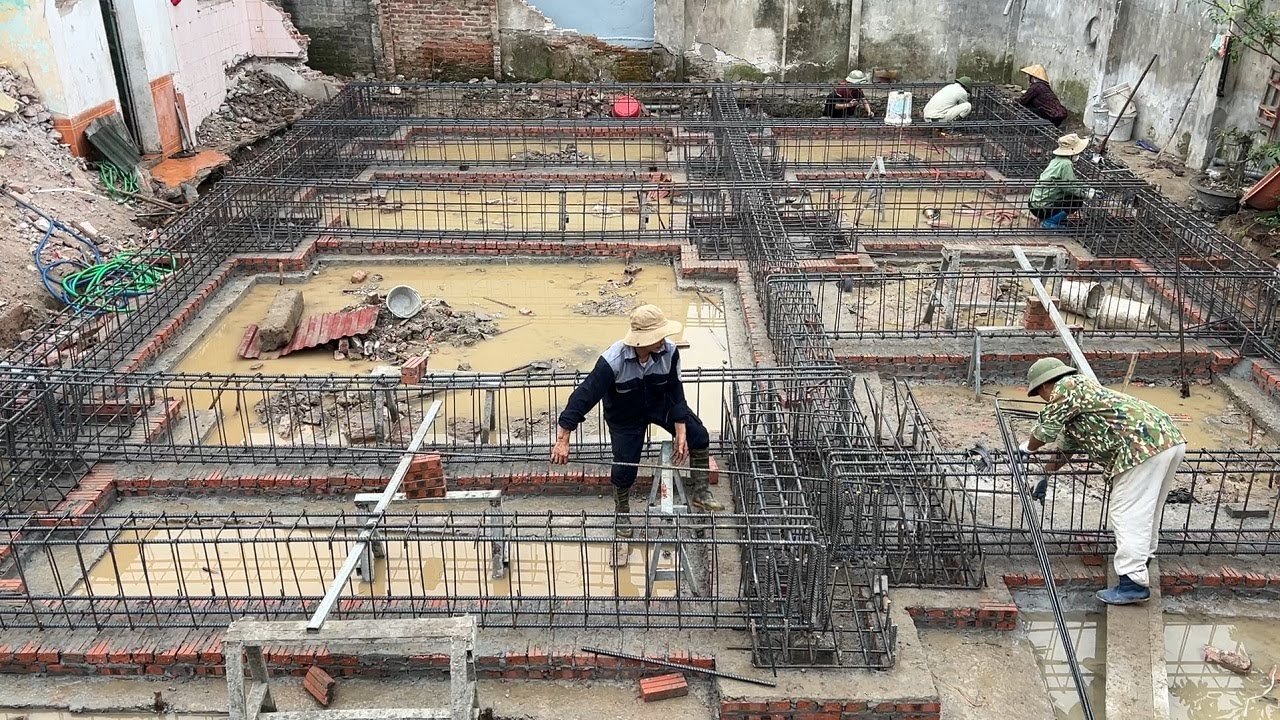
Structural engineering is a critical discipline within the field of civil engineering, focusing on the design and analysis of structures that support or resist loads. In building design, structural engineers play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, stability, and durability of structures. They collaborate with architects to create designs that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing while adhering to safety regulations and building codes.
Structural engineers evaluate the strength of materials, the impact of environmental forces, and the overall integrity of the building framework. They use advanced software and analytical methods to simulate loads and stresses, ensuring that the structure can withstand various forces such as wind, earthquakes, and human use.
By carefully selecting materials and designing structural elements like beams, columns, and foundations, structural engineers optimize the use of resources, contributing to the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of the building. Their expertise ensures that buildings can perform their intended functions safely over their lifespan, accommodating changes and expansions if necessary.
Overall, the role of structural engineering in building design is indispensable, as it merges technical proficiency with creative problem-solving to bring architectural visions to life while prioritizing safety and functionality.
Introduction
Structural engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering that plays a critical role in the design and construction of buildings. It focuses on the framework of structures and ensuring that they can withstand the loads and forces they encounter throughout their lifespan. This article delves into the essential aspects of structural engineering, its principles, and its significance in building design.
The Fundamentals of Structural Engineering
Understanding Structures
At its core, structural engineering is concerned with the design and analysis of buildings, bridges, towers, and other structures. Engineers in this field must ensure that these structures are safe, stable, and capable of performing their intended functions. This involves understanding the behavior of various materials, the effects of loads and forces, and the interaction between different structural components.
Materials Used in Structural Engineering
Structural engineers work with a variety of materials, each with its properties and uses. Common materials include:
- Concrete: Known for its compressive strength, concrete is used extensively in construction for its durability and versatility.
- Steel: Valued for its tensile strength and flexibility, steel is often used in combination with concrete to provide support and reinforcement.
- Timber: Used in residential and certain commercial buildings, timber offers a sustainable option with adequate strength for many applications.
Load Analysis
Structural engineers must conduct a thorough analysis of the loads that a structure will encounter. These loads can be broadly categorized into:
- Dead Loads: Permanent or static forces such as the weight of the structure itself.
- Live Loads: Temporary or dynamic forces including people, furniture, and vehicles.
- Environmental Loads: Forces from natural phenomena such as wind, earthquakes, snow, and temperature changes.
Design Principles in Structural Engineering
Safety and Stability
One of the primary goals of structural engineering is to ensure the safety and stability of a building. This is achieved through meticulous planning and adherence to design codes and standards that govern aspects such as load-bearing capacity, material usage, and construction techniques.
Structural Integrity
Structural integrity refers to the ability of a structure to withstand its intended load without experiencing failure. Engineers must design structures that can endure various stresses and strains over time, taking into account factors such as fatigue, corrosion, and material degradation.
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
While safety is paramount, structural engineers must also consider efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This involves optimizing the use of materials and construction methods to achieve the desired strength and stability without unnecessary expenditure.
Aesthetics and Functionality
Structural engineering is not solely about technical specifications; it also involves the aesthetic and functional aspects of a building. Engineers collaborate with architects to ensure that the structural components support the architectural vision while maintaining functionality.
Innovations in Structural Engineering
Advanced Materials
The development of advanced materials has significantly impacted structural engineering. High-performance concrete, composite materials, and innovative steel alloys allow for lighter, stronger, and more durable structures.
Computational Tools
The use of computational tools and software has revolutionized structural engineering. Finite element analysis (FEA), building information modeling (BIM), and other digital tools enable engineers to simulate and optimize designs with greater accuracy and efficiency.
Sustainable Design
Sustainability is a growing concern in structural engineering. Engineers are increasingly focused on designing buildings that minimize environmental impact through energy efficiency, the use of sustainable materials, and innovative construction techniques.
The Role of Structural Engineers in Construction
Collaboration with Other Disciplines
Structural engineers work closely with architects, mechanical engineers, electrical engineers, and construction managers to ensure the successful completion of a project. This interdisciplinary collaboration is crucial for addressing the various challenges that arise during the design and construction phases.
Site Assessment and Preparation
Before construction begins, structural engineers perform site assessments to evaluate soil conditions, topography, and other factors that influence the design and construction process. This information is vital for developing foundations and other structural elements.
Construction Oversight
During construction, structural engineers provide oversight and guidance to ensure that the design specifications are adhered to. They conduct inspections, address unforeseen issues, and make adjustments as necessary to maintain the integrity and safety of the structure.
Case Studies: Iconic Structures
The Burj Khalifa
The Burj Khalifa in Dubai exemplifies the pinnacle of structural engineering. Standing at over 828 meters, it is the tallest building in the world. Its design incorporates innovative structural systems and materials to withstand the extreme wind forces and seismic activity in the region.
The Sydney Opera House
The Sydney Opera House is a testament to the collaboration between architects and structural engineers. Its distinctive shell-like design presented unique challenges that were overcome through advanced engineering techniques, resulting in a world-renowned architectural masterpiece.
Challenges in Structural Engineering
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods pose significant challenges for structural engineers. Designing structures that can withstand these events requires a deep understanding of their dynamics and the implementation of appropriate safety measures.
Urbanization and Population Growth
The rapid pace of urbanization and population growth demands innovative structural solutions to accommodate increasing densities and the need for sustainable development. Engineers must balance these demands with environmental and economic considerations.
Technological Advancements
While technological advancements offer new opportunities, they also present challenges in keeping up with evolving design tools, materials, and construction methods. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for engineers to remain effective in their roles.
Conclusion
Structural engineering is a vital component of building design and construction, ensuring that structures are safe, stable, and functional. Through the application of engineering principles, innovative materials, and collaborative efforts, structural engineers contribute significantly to the built environment. As the industry continues to evolve, these professionals will play a crucial role in addressing future challenges and shaping the landscapes of tomorrow.
Book Recommend Structural engineering
- “Structural Engineering: A Very Short Introduction” by David Blockley
- “Structural Analysis” by R.C. Hibbeler
- “Design of Reinforced Concrete” by Jack C. McCormac and Russell H. Brown
- “Structural Steel Design” by Jack C. McCormac and Stephen F. Csernak
- “Building Structures” by James Ambrose and Patrick Tripeny
- “Principles of Structural Design: Wood, Steel, and Concrete” by Ram S. Gupta
- “Structural Engineering Handbook” by Edwin H. Gaylord, Charles N. Gaylord, and James E. Stallmeyer
- “Advanced Structural Analysis” by Ashok K. Jain
- “Form and Forces: Designing Efficient, Expressive Structures” by Edward Allen and Waclaw Zalewski
- “Structural Design from First Principles” by Michael Byfield
FAQ: Structural Engineering
Structural engineering is a branch of civil engineering focused on the design and analysis of structures that support or resist loads. This includes buildings, bridges, towers, and other infrastructure.
Structural engineering ensures that structures are safe, stable, and durable. It plays a crucial role in preventing structural failures and ensuring the longevity and safety of buildings and infrastructure.
Structural engineers are responsible for designing structures that can withstand various forces and loads. They analyze the strength and stability of structures, select appropriate materials, and ensure that designs comply with building codes and regulations.
Structural engineers work with a variety of materials including concrete, steel, wood, masonry, and composites. The choice of material depends on the structure’s requirements, environment, and cost considerations.
Safety is ensured through rigorous analysis and testing, adherence to building codes and standards, and the use of safety factors in design. Engineers also consider potential risks such as natural disasters and human-induced events.
Structural engineers use software tools like AutoCAD, SAP2000, ETABS, and Revit for designing and modeling structures. These tools help in analyzing complex loads, simulating structural behavior, and creating detailed construction drawings.
Civil engineering is a broad field that encompasses various sub-disciplines including structural engineering. Structural engineering specifically focuses on the design and analysis of structures, while civil engineering covers a wider range of areas such as transportation, water resources, and geotechnical engineering.
Structural engineers contribute to sustainability by designing energy-efficient buildings, using sustainable materials, and implementing innovative construction methods that reduce waste and environmental impact.
In earthquake-prone areas, structural engineers design buildings to withstand seismic forces. This involves using special construction techniques and materials to absorb and dissipate energy, reducing the risk of collapse during an earthquake.
To become a structural engineer, one typically needs a bachelor’s degree in civil or structural engineering, followed by gaining practical experience through internships or entry-level positions. Professional licensure may also be required, which involves passing exams and fulfilling experience requirements.

