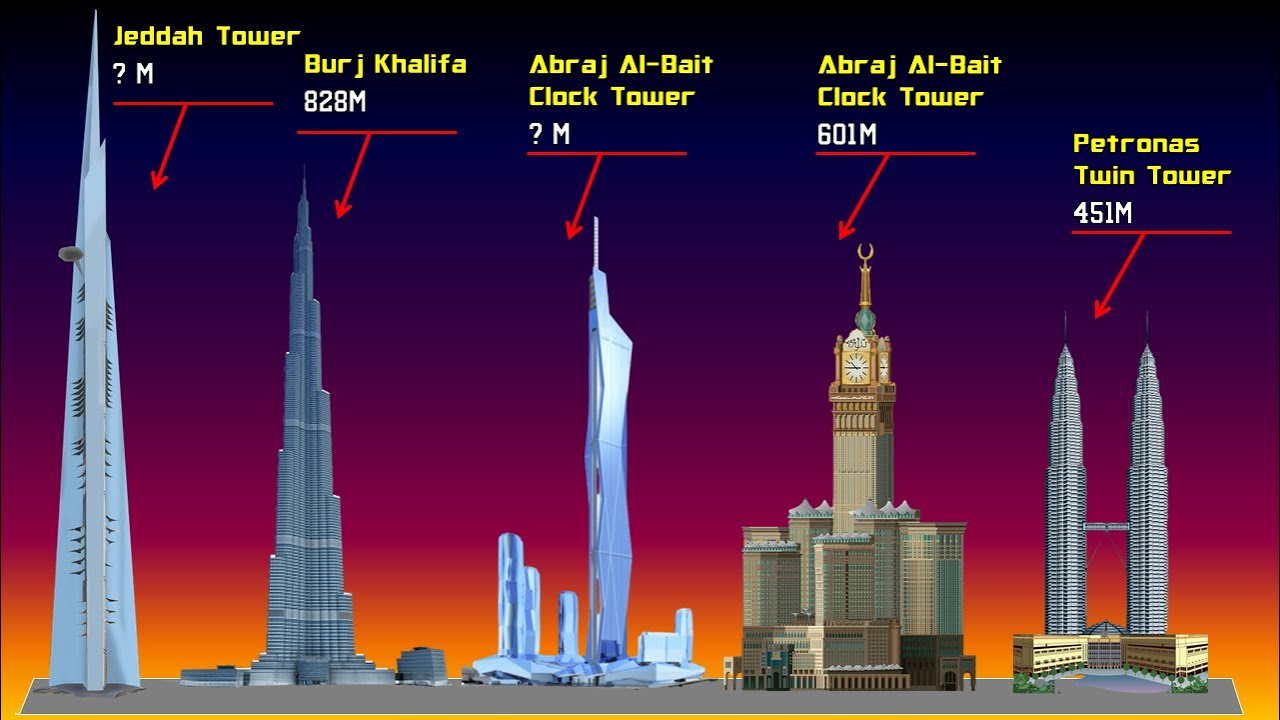
Electrical engineering have helped develop the infrastructure required to transmit and distribute electricity to every nook and cranny of home and business. Electrical engineers are responsible for everything from the design and construction of power lines, substations, and transformers.
Introduction
Electrical engineering is a dynamic and integral field of engineering that focuses on the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. Originating in the late 19th century with the commercialization of electric power supply, electrical engineering has evolved, powering technological advancements and playing a pivotal role in modern society. This article delves into the multifaceted world of electrical engineering, exploring its history, core principles, sub-disciplines, and its impact on our daily lives and future innovations.

Historical Background
The roots of electrical engineering can be traced back to notable figures such as Michael Faraday, James Clerk Maxwell, and Nikola Tesla, whose groundbreaking work in electromagnetism laid the foundation for modern electrical technology. The development of the electric telegraph and the practical use of electricity for lighting and power in the late 1800s marked the beginning of the electrical engineering discipline as we know it today. Thomas Edison and George Westinghouse’s contributions during the “War of Currents” further propelled the field, with Edison’s direct current (DC) system competing against Westinghouse’s alternating current (AC) system, ultimately establishing AC as the dominant method for electricity transmission.
Core Principles of Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is built upon several core principles and concepts:
- Voltage, Current, and Resistance: At the heart of electrical engineering lies Ohm’s Law, which relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit: V = IR. Understanding these fundamental concepts is crucial for analyzing and designing electrical circuits.
- Power and Energy: Power, measured in watts, is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. Energy, measured in joules, is the capacity to do work. These concepts are key in designing efficient electrical systems.
- Circuit Theory: This involves the study of how electrical circuits function, including the analysis of series and parallel circuits, the use of Kirchhoff’s laws, and the application of Thevenin’s and Norton’s theorems.
- Electromagnetism: This principle encompasses the study of electric fields, magnetic fields, and how they interact. It is essential in the design of motors, transformers, and inductors.
- Signal Processing: The analysis, manipulation, and transformation of signals is a crucial aspect of electrical engineering, enabling the development of communication systems, audio processing, and more.
Sub-disciplines of Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is a broad field, encompassing various sub-disciplines, each with its own specialized focus:
- Power Engineering: This sub-discipline deals with the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. It involves the design of power plants, electrical grids, transformers, and renewable energy systems, ensuring a reliable and efficient power supply.
- Control Systems: Control engineering focuses on the modeling and design of dynamic systems and controllers to manage and regulate the behavior of systems such as autopilot in aircraft, industrial automation, and robotics.
- Electronics: This area involves the design and development of electronic circuits, devices, and systems, including semiconductors, transistors, and integrated circuits that form the backbone of modern electronics.
- Communications: Communication engineering focuses on the transmission and reception of signals and data. It encompasses the design of communication networks, wireless systems, and protocols that enable global connectivity.
- Microelectronics: This sub-discipline deals with the design and fabrication of very small electronic components and systems, including microprocessors and memory chips, which are critical in the advancement of computer technology.
- Instrumentation: Instrumentation engineering focuses on the design and development of devices that measure physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, and flow, essential for monitoring and controlling industrial processes.
Impact on Daily Life
Electrical engineering has a profound impact on our daily lives, often in ways we may not immediately recognize. Here are some examples of how electrical engineering powers our world:
- Home Appliances: From refrigerators to washing machines, electrical engineering has transformed household chores, making them more efficient and convenient.
- Transportation: Electrical engineering plays a crucial role in the development of electric vehicles, trains, and aircraft, contributing to cleaner and more sustainable transportation solutions.
- Communication: The internet, smartphones, and other communication devices are all products of electrical engineering, enabling instant communication and information sharing worldwide.
- Healthcare: Medical devices such as MRI machines, pacemakers, and diagnostic equipment are designed and operated using principles of electrical engineering, enhancing patient care and medical research.
- Renewable Energy: Electrical engineers are at the forefront of developing technologies that harness renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Future of Electrical Engineering
As technology continues to advance, electrical engineering will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future. Here are some emerging trends and areas of focus:
- Smart Grids: The development of smart grids, which use digital technology to monitor and manage electricity demand efficiently, is a key area of research, aiming to enhance the reliability and sustainability of power systems.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT involves connecting everyday objects to the internet, enabling real-time data exchange and automation. Electrical engineers are crucial in designing the sensors, networks, and systems that make IoT possible.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: These technologies are becoming integral in the design and optimization of electrical systems, from predictive maintenance in power plants to autonomous vehicles and smart home devices.
- Quantum Computing: Electrical engineers are exploring the potential of quantum computing, which promises to revolutionize computing power and solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
- Sustainable Energy Solutions: Continued research and innovation in renewable energy technologies and energy storage solutions are essential to meet the growing demand for clean and sustainable energy.
Conclusion
Electrical engineering is an ever-evolving field that continues to drive technological progress and improve the quality of life across the globe. With its diverse sub-disciplines and wide-ranging applications, electrical engineering is integral to addressing some of the world’s most pressing challenges, from sustainable energy to advanced communication systems. As we look to the future, the role of electrical engineering in powering our world will only become more significant, paving the way for new innovations and breakthroughs that will shape the 21st century and beyond.